Xi Ursae Majoris on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Xi Ursae Majoris is a
 The two components are yellow
The two components are yellow  Each component of this double star is itself a single-lined
Each component of this double star is itself a single-lined
 ξ Ursae Majoris is classified as an
ξ Ursae Majoris is classified as an
(Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 6 月 21 日
/ref>
Animation of the orbits of the stars in the Alula Australis System at SolStation.com
by Dr. Jim Kaler. {{Stars of Ursa Major F-type main-sequence stars G-type main-sequence stars M-type main-sequence stars T-type stars Ursae Majoris, Xi RS Canum Venaticorum variables Emission-line stars Spectroscopic binaries 4 Ursa Major (constellation) Ursae Majoris, Xi 4374 5 Durchmusterung objects Ursae Majoris, 53 0423 098230 1 055203 Alula Australis WISE objects
star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a '' star cluster'' or '' galaxy'', although, broadly speak ...
in the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
of Ursa Major
Ursa Major (; also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear," referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa ...
. It has the traditional name Alula Australis; ''Xi Ursae Majoris'' is the Bayer designation, which is Latinised from ξ Ursae Majoris and abbreviated Xi UMa or ξ UMa. It was the first visual double star for which an orbit was calculated, when it was computed by Félix Savary in 1828. It is also a variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as ...
with a small amplitude. Xi Ursae Majoris is found in the left hind paw of the Great Bear.
Stellar system
 The two components are yellow
The two components are yellow main-sequence star
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hert ...
s. The brighter component (designated Xi Ursae Majoris A), has a mean apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's li ...
of +4.41. The companion star (Xi Ursae Majoris B) has an apparent magnitude of +4.87. The orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
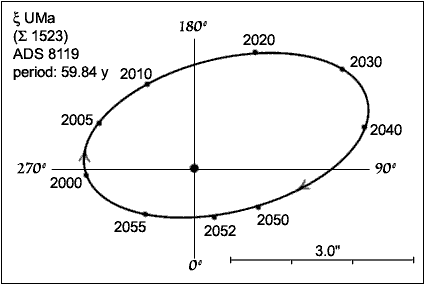
of the two stars is 59.84 years. They are currently (2022) separated by 2.3 arcseconds, and will widen to a maximum 3.0 arcseconds in 2035.
 Each component of this double star is itself a single-lined
Each component of this double star is itself a single-lined spectroscopic binary
A binary star is a system of two star, stars that are gravity, gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separa ...
. The orbit of the A pair has been determined from spectroscopy and speckle interferometry
Speckle imaging describes a range of high-resolution astronomical imaging techniques based on the analysis of large numbers of short exposures that freeze the variation of atmospheric turbulence. They can be divided into the shift-and-add ("'' ...
, giving a period of 669 days and an eccentricity of 0.53. B's binary companion (Xi Ursae Majoris Bb) has not been detected visually or spectroscopically, but the radial velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity, also known as radial speed or range rate, of a target with respect to an observer is the temporal rate of change, rate of change of the distance or Slant range, range between the two points. It is e ...
variations of the spectral lines show a circular orbit with a period of 3.98 days. The masses of both A and B's companions (Ab and Bb) (deduced by the sum total mass of the system minus the likely masses of Aa and Ba determined by their class) indicate that they are probably red dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave since 2009, gaining a cult following. T ...
s, Bb being on the cool end of the M spectrum, not much hotter than a brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs (also called failed stars) are substellar objects that are not massive enough to sustain nuclear fusion of ordinary hydrogen ( 1H) into helium in their cores, unlike a main-sequence star. Instead, they have a mass between the most ...
.
In 2012 Wright et al. discovered the fifth component and the second brown dwarf (if Bb is also a brown dwarf) of the system using Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE, observatory code C51, Explorer 92 and SMEX-6) is a NASA infrared astronomy space telescope in the Explorers Program. It was launched in December 2009, and placed in hibernation mode in February 2011, ...
(WISE) data—a T8.5 brown dwarf WISE J111838.70+312537.9 with angular separation 8.5 arcmin
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The n ...
, and the projected physical separation about 4,000 AU.
Variable star
 ξ Ursae Majoris is classified as an
ξ Ursae Majoris is classified as an RS Canum Venaticorum variable An RS Canum Venaticorum variable is a type of variable star. The variable type consists of close binary stars having active chromospheres which can cause large stellar spots. These spots are believed to cause variations in their observed luminosi ...
and its brightness varies by 0.01 magnitude. Component B is believed to be the variable star, showing characteristic emission line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to iden ...
s in its spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors i ...
that are not present for component A.
Nomenclature
''ξ Ursae Majoris'' ( Latinised to ''Xi Ursae Majoris'') is the star's Bayer designation. It also bore the traditional names ''Alula Australis'' (and erroneously ''Alula Australe''). ''Alula'' (shared withNu Ursae Majoris
Nu Ursae Majoris (ν Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Nu UMa, ν UMa), formally named Alula Borealis , is a double star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. At an apparent visual magnitude of +3.490, it is br ...
) comes from the Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
phrase 'the First Spring' and ''Australis'' is Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for 'southern'. In 2016, the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ...
organized a Working Group on Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education ...
(WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included ''Alula Australis'' for this star.
In Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, (), meaning ''Three Steps
3 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
3, three, or III may also refer to:
* AD 3, the third year of the AD era
* 3 BC, the third year before the AD era
* March, the third month
Books
* '' Three of Them'' (Russian: ', literally, "three"), a 1901 ...
'', refers to an asterism consisting of Xi Ursae Majoris, Iota Ursae Majoris
Iota Ursae Majoris (ι Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Iota UMa, ι UMa), also named Talitha , is a star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.14, making it v ...
, Kappa Ursae Majoris
Kappa Ursae Majoris (κ Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Kappa UMa, κ UMa) is a binary star in the constellation of Ursa Major. With a combined apparent magnitude of +3.60, the system is approximately 358 light-years from Ear ...
, Lambda Ursae Majoris
Lambda Ursae Majoris (λ Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Lambda UMa, λ UMa), formally named Tania Borealis , is a star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major.
Properties
This star has an apparent visual magni ...
, Mu Ursae Majoris
Mu Ursae Majoris (μ Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Mu UMa, μ UMa), formally named Tania Australis , is a binary star in the constellation of Ursa Major. An apparent visual magnitude of +3.06 places it among the brighter m ...
and Nu Ursae Majoris
Nu Ursae Majoris (ν Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Nu UMa, ν UMa), formally named Alula Borealis , is a double star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. At an apparent visual magnitude of +3.490, it is br ...
. Consequently, the Chinese name
Chinese names or Chinese personal names are names used by individuals from Greater China and other parts of the Chinese-speaking world throughout East and Southeast Asia (ESEA). In addition, many names used in Japan, Korea and Vietnam are often a ...
for Xi Ursae Majoris itself is (, en, Star of Second Lower Step)./ref>
See also
* List of star systems within 25–30 light-yearsReferences
Note
External links
Animation of the orbits of the stars in the Alula Australis System at SolStation.com
by Dr. Jim Kaler. {{Stars of Ursa Major F-type main-sequence stars G-type main-sequence stars M-type main-sequence stars T-type stars Ursae Majoris, Xi RS Canum Venaticorum variables Emission-line stars Spectroscopic binaries 4 Ursa Major (constellation) Ursae Majoris, Xi 4374 5 Durchmusterung objects Ursae Majoris, 53 0423 098230 1 055203 Alula Australis WISE objects